Circuit breakers open and close the flow of the electric circuit, which regulates the current flow. A breaker’s overloading can result in malfunctioning of the system. These problems can be avoided by knowing the amp load that a circuit breaker can handle.
The term ‘amp load’ refers to the maximum amount of power that can be safely extracted from a power-generating unit or a transformer.
The age of the building and the kind of system installed in it determines the amp loads. While newer homes normally have over 100 amps of service, larger and more contemporary homes typically have 200 to 400 amps of service, and older homes may have services with an amp load of 30 to 60 amps.
A 50 Amp Breaker can handle a current of up to 50 Amperes, while a 40 Amp Breaker can handle a current of up to 40 Amperes.
Differences: 50 Amp Breaker & 40 Amp Breaker
The differences between the 50 amp breaker and the 40 amp breaker can be seen below in the 50 amp breaker wiring diagram and the 40 amp breaker wiring diagram, respectively.
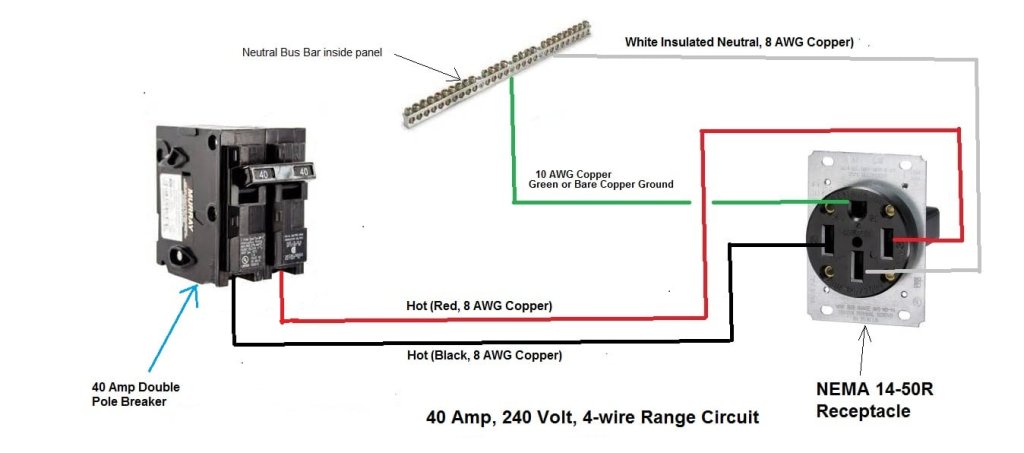

How to Know if Your Circuit Breaker Is 40 Amp or 50 Amp?
You can refer to the following tips to determine whether your circuit breaker is 40 amp or 50 amp.
1. Check the Label
The easiest way to figure out the amp load of your circuit breaker is to check the label on the breaker itself. Usually, the label is present on the front, or the side of the breaker, and the amperage value is clearly stated on it. The label might be marked with ‘40A’ or ‘50A’ to indicate the amperage rating of 40 amp or 50 amp, respectively.
2. Check the Electrical Panel
If you are unable to find the label or are not able to read it, you can check the electrical panel where the breaker is installed. Each breaker should ideally be marked with the amperage rating along the breaker slot or on the panel’s directory. This directory helps you identify which breaker belongs to which area or appliance.
3. Inspect the Wiring
If you have some electric knowledge and can identify objects, you can even try to identify the wiring of the breaker. Typically, a 50-amp circuit breaker is used with larger gauge (thicker) wires than a 40-amp breaker. The wire gauge can often be seen on the insulation of the wire itself. However, this method is not foolproof and requires knowledge.
4. Single Pole or Double Pole
A 40 amp breaker is usually a single-pole breaker, occupying only one slot in the panel. Single-pole breakers are commonly used for general household circuits. Whereas a 50 amp breaker is often a double-pole breaker, meaning it occupies two adjacent slots in the electrical panel. Double-pole breakers are used for higher voltage circuits, like those powering electric ranges or air conditioning units.
5. Handle Design or Color
A lot of manufacturers color-code their breakers. The handle design and the color of the 40 amp breaker and the 50 amp breaker will be different. In this case, you will need to find out if the manufacturer of your breakers put this technique to use.
6. Consult a Professional
If you still think you cannot identify the amperage circuit breaker or do not understand how to do it, you can always consult a professional electrician. They have the expertise to quickly and accurately determine the amperage rating of the breaker, ensuring safety and compliance with electrical codes.
You should remember that it is very important to identify the amperage of the circuit breaker to maintain the safety and efficiency of your electric system. Using the wrong amperage breaker can lead to overheating, potential fires, and other hazardous situations. If in doubt, it’s always better to seek professional help.
How to Calculate the Electric Load Capacity of Your Breaker
Each circuit breaker can handle a certain amount of current or amperage. The breaker itself has a label indicating this grade. It is important to keep in mind that circuit breakers are only capable of handling roughly 80% of their total amperage. According to this, a 40 amp circuit breaker can withstand roughly 32 amps, compared to a 50 amp circuit breaker’s capacity of about 40 amps.
Steps to Calculate
1. Find the circuit breaker for the electrical appliance you are operating, which is typically a 40-amp or 50-amp circuit.
2. Add 0.8 to the amperage. This is so that a circuit breaker doesn’t operate at over 80% of its maximum amperage. If you do not do this, it could result in calculating errors or, worse yet, electrical fires!
3. Determine the circuit’s total amperage requirements for ALL the devices you intend to connect.
You should remember that while it is important to use the correct level of the amperage with the breaker capable of handling its power, for emergencies, a higher level of breaker can be used for the lower amperage. This will eventually lead to malfunctioning of the electric system, but it will not happen immediately and will hold out during emergencies for a short period. However, under no circumstances should a breaker of lower capacity handle higher amperage because that could lead to electric fires and short circuits and can be extremely dangerous.
Concluding Thoughts
Understanding the differences and traits of individual breakers is very important to protect the electric system from hazards and malfunctions and to keep it maintained and balanced. We may learn more about the capacity of power-generating units and transformers by being familiar with the concept of “amp load,” which indicates the maximum limit that can be extracted from a breaker.
The individual traits of 50 amp breakers and 40 amp breakers and the difference between the two have been explained in detail, and you will now be able to identify both easily and determine what the amperage of your breaker is.

